Heap Exploit - House of Lore (a.k.a. Smallbin attack)
House of Lore
malloc 함수의 smallbin에 해당하는 chunk의 재할당과 smallbin에 배치하는 과정을 이용한 공격 기법이다.
[1] [2] [3]
제약 조건
1. Smallbin에 들어간 chunk의 bk를 조작할 수 있음
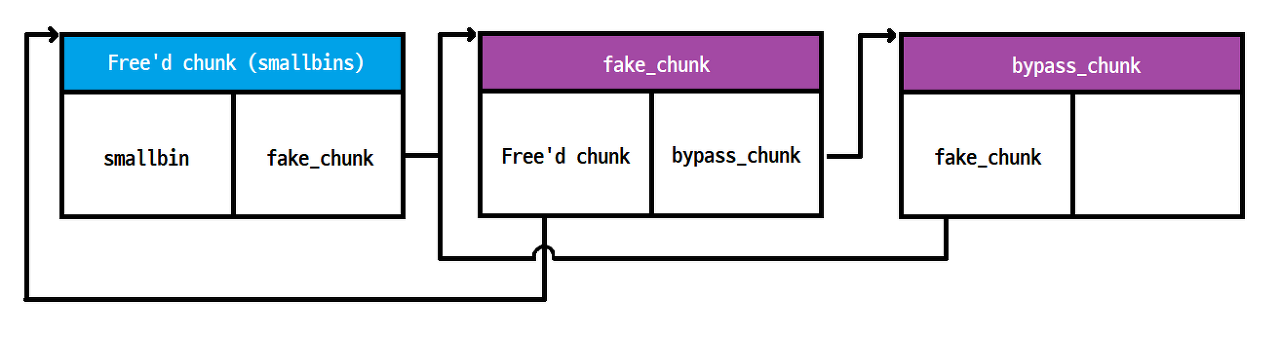
2. 다음과 같은 구성을 만들어야 함(= Heap leak이 선행됨)
소스 코드와 함께 파악하는 원리
glibc 2.23 / malloc.c [4]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
if ((victim = last (bin)) != bin)
{
if (victim == 0) /* initialization check */
malloc_consolidate (av);
else
{
bck = victim->bk;
if (__glibc_unlikely (bck->fd != victim))
{
errstr = "malloc(): smallbin double linked list corrupted";
goto errout;
}
set_inuse_bit_at_offset (victim, nb);
bin->bk = bck;
bck->fd = bin;
if (av != &main_arena)
victim->size |= NON_MAIN_ARENA;
check_malloced_chunk (av, victim, nb);
void *p = chunk2mem (victim);
alloc_perturb (p, bytes);
return p;
}
}
last(bin)은 bin->bk를 의미한다. 즉, 가장 위 조건문은 bin->bk != bin를 검사하는 구문이고, bin->bk == bin은 해당 smallbin에 free’d chunk가 없다는 것을 의미한다.
그 외에 추가적인 조건문은 victim->bk->fd == victim을 맞춰주기만 하면 된다. bypass_chunk가 존재하는 이유가 바로 여기서 드러난다. smallbin에 들어간 fake_chunk를 다시 할당하기 위해서는 fake_chunk->bk->fd == fake_chunk가 되어야 하기 때문이다.
이 조건만 만족해준다면, 공격자는 임의의 주소에 위치한 청크인 fake_chunk를 smallbin에서 재할당하여 사용할 수 있게 된다.
glibc 2.26~ / malloc.c [5]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
if ((victim = last (bin)) != bin)
{
bck = victim->bk;
if (__glibc_unlikely (bck->fd != victim))
malloc_printerr ("malloc(): smallbin double linked list corrupted");
set_inuse_bit_at_offset (victim, nb);
bin->bk = bck;
bck->fd = bin;
if (av != &main_arena)
set_non_main_arena (victim);
check_malloced_chunk (av, victim, nb);
#if USE_TCACHE
/* While we're here, if we see other chunks of the same size,
stash them in the tcache. */
size_t tc_idx = csize2tidx (nb);
if (tcache && tc_idx < mp_.tcache_bins)
{
mchunkptr tc_victim;
/* While bin not empty and tcache not full, copy chunks over. */
while (tcache->counts[tc_idx] < mp_.tcache_count
&& (tc_victim = last (bin)) != bin)
{
if (tc_victim != 0)
{
bck = tc_victim->bk;
set_inuse_bit_at_offset (tc_victim, nb);
if (av != &main_arena)
set_non_main_arena (tc_victim);
bin->bk = bck;
bck->fd = bin;
tcache_put (tc_victim, tc_idx);
}
}
}
#endif
void *p = chunk2mem (victim);
alloc_perturb (p, bytes);
return p;
}
glibc 2.26 이상부터는 tcache가 생겼기 때문에, smallbin을 할당하는 루틴 중에 smallbin에 위치한 free’d chunk들을 같은 size의 tcache_entry로 이동시키는 루틴이 생겼다.
while 반복문을 돌면서, tcache entry가 모두 채워지거나, smallbin에 아무런 free’d chunk가 없을 때까지 tcache_put 함수를 실행하려고 한다. 따라서, glibc 2.23 때와 같이, fake_chunk와 bypass_chunk 딱 2개만 만들면, tcache로 옮기는 과정에서 segmentation fault가 반드시 발생하게 된다.
1. tcache->counts[tc_idx] < mp_.tcache_count
이를 우회하기 위해서는 tcache를 모두 채울 만큼 충분한 개수(7개)의 fake_chunk를 만들면 된다.
전자를 만족시켰다면(tcache entry가 모두 채워짐), 공격자는 가장 나중에 tcache에 배치됐으면서, 임의의 주소에 위치한 청크인 fake_chunk를 재할당할 수 있게 된다.
2. (tc_victim = last (bin)) != bin
그런데, 후자를 만족시키면서(smallbin에 아무런 free’d chunk가 없음), 비슷한 결과를 내는 방법이 있다.
libc leak을 이미 성공한 이후라면, bypass_chunk->bk를 smallbin으로 만들면 되지만, 그렇지 않다면 다음의 방법을 이용하면 된다.
세 개의 chunk를 smallbin에 둔 상태이고, 가운데 위치한 chunk->bk를 fake_chunk로 만들고, fake_chunk->bk에는 원래 chunk->bk를 넣는다. 이는 smallbin에 위치한 chunk를 tcache에 넣을 때, 검사가 부재하다는 것을 이용한 방법으로, 결국 마지막 smallbin에 위치한 chunk의 bk 값은 smallbin이기 때문에 while문을 탈출할 수 있게 된다. [6]
더욱 자세한 설명은 이 블로그에서 보면 되겠다.
전자의 방법은 smallbin이 망가진다는 단점이 있으나, 후자의 방법은 그러한 단점이 없다.
Reference
[1] shellphish, “how2heap”, https://github.com/shellphish/how2heap/blob/master/glibc_2.27/house_of_lore.c
[2] Lazenca, “The House of Lore[Korean]”, https://www.lazenca.net/pages/viewpage.action?pageId=1148020
[3] dokydoky, “[Heap Exploitation] Smallbin attack”, https://dokydoky.tistory.com/461
[4] bootlin, “glibc-2.23 malloc.c”, https://elixir.bootlin.com/glibc/glibc-2.23/source/malloc/malloc.c
[5] bootlin, “glibc-2.27 malloc.c”, https://elixir.bootlin.com/glibc/glibc-2.27/source/malloc/malloc.c
[6] OSORI, “tcache smallbin 취약점”, https://osoriselfmanage.tistory.com/96?category=916275